| |||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
| Capillary Pressure of Pressure Solution Seam-based Faults in Carbonates | |||||||
|
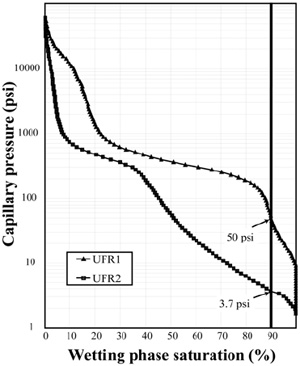
Agosta (2006) and Agosta et al. (2007) presented capillary pressure results from mercury injection analysis of two uncemented fault rock samples from fault cores of a normal fault in platform carbonates, Fucino Basin, Central Italy. The breakthrough pressure is taken as the mercury-air capillary pressure that corresponds to 10% of cumulative intruded mercury. This pressure is 349 MPa (50 Psi) for one sample and 25.5 MPa (3.7 Psi) for the other (Figure 1). The seal potentials are 77 and 5.7 m for gas and 140 and 10.4 m for oil.
| |||||||
| Reference: |
|||||||
| Agosta, F., 2006 Agosta, F., Parasad, M., Aydin, A., 2007 |
|||||||
|
Readme | About Us | Acknowledgement | How to Cite | Terms of Use | Ⓒ Rock Fracture Knowledgebase |
|||||||