| |||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
| Grain Size Distribution of Fault Rock in Dynamic Faulting | |||||||
|
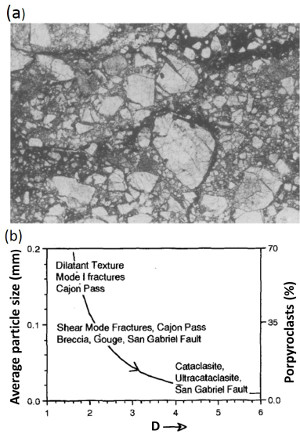
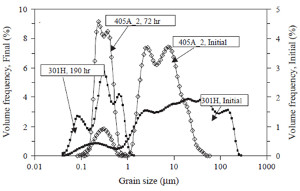
In search of information for earthquake faulting, well-known active faults and their components have been investigated by many scientists. The availability of drill holes and cores from some of these faults provided an additional advantage of avoiding near surface effects. The study by Blenkinsop (1991) is one of those earlier studies. Blenkinsop identified grain sizesunder 0.01 mm (Figure 1(a) and (b)) in core samples from faults of the San Andreas Fault system and attributed them to cataclastic and ultracataclastic processes (Figure 1(b). He also suggested that as the grain size decreases, the fractal dimension increases. Also see Sammis et al. (1986) on the fractal nature of rock fragmentation. Recently, efforts have been made to identify specific mechanism(s) responsible for extreme fragmentation of fault rock also referred to as pulverization (Reches and Drewers, 2005; Sammis and Ben-Zion, 2008; Doan and Gary, 2009; and Yuan et al., 2011). Figure 2 is from Reches and Drewer showing extreme grain size reduction in two samples; one from the San Andreas at the Tejon Pass, California and the other from a newly formed fault in a South African gold mine. The authors interpreted the extreme grain size reduction or pulverization in terms of the advancing stress field at the tip of a dynamic fault and its spatial and temporal variation from tensile to compression as the rupture front propagates. Similarly, controlled laboratory experiments by Yuan et al. (2011) among others provided laboratory data for loading conditions for favoring deformation mode for pulverization. | |||||||
| Reference: |
|||||||
| Blenkinsop, T.G., 1991 Doan, M.L., Gary, G., 2009 Reches, Z., Dewers, T.A., 2005 Sammis, C.G., Osborne, R.H., Anderson, J.L., Badert, M., White, P., 1986 Sammis, C.G., Ben-Zion, Y., 2008 Yuan, F., Prakash, V., Tullis, T., 2011 |
|||||||
|
Readme | About Us | Acknowledgement | How to Cite | Terms of Use | Ⓒ Rock Fracture Knowledgebase |
|||||||