| |||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
| Faulting by Shearing of Pressure Solution Seams | |||||||
|
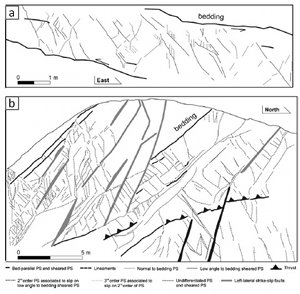
A particular category of weakness-based faults initiates from shearing of pressure solution seams which formed earlier. Shearing of pressure solution seams produces splays around their tip regions where stresses concentrate. The splays are most commonly splay pressure solution seams but splay joints-veins are also observed. For mixed modes of splays, please refer to the sections 'Splay Pressure Solution Seams,' 'Splay Joints,' and 'Faulting by Shearing of Vein and Pressure Solution Seam Assemblages' for more information about these processes. Shearing of a set of pressure solution seams results in a set of sheared pressure solution seams linked by either splay pressure solution seams (Figure 1), or splay joints-veins or both (Figure 2).
Like other types of weakness-based faults, sheared pressure solution seam-based faults grow by successive splays and subsequent shearing of the second and higher order splays producing normal (Graham et al., 2003), thrust, and strike-slip faults (Antonellini et al., 2008 and Aydin et al., 2010) (Figure 3). | |||||||
| Reference: |
|||||||
| Antonellini, M., Tondi, E., Agosta, F., Aydin, A., Cello, G., 2008 Aydin, A., Antonellini, M., Tondi, E., Agosta, F., 2010 Graham Wall, B., Antonellini, M., Aydin, A., 2003 |
|||||||
|
Readme | About Us | Acknowledgement | How to Cite | Terms of Use | Ⓒ Rock Fracture Knowledgebase |
|||||||