| |||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
| Mirror and Mist | |||||||
|
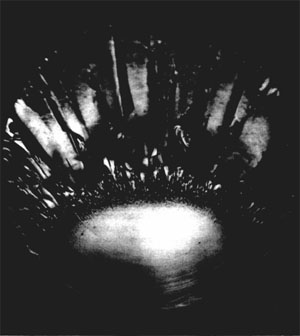
Mirror refers to a smooth morphology on a joint surface and mist refers to the near-smooth frosted zone (Figure 1). Mirror and mist are commonly confined in a small area around the initiation point and interpreted to occur at low propagation velocity. When the propagation velocity becomes high and the local stress is perturbed, hackle marks, rib marks, and fringe joints will occur. | |||||||
| Reference: |
|||||||
| Johnson, A.M., Holloway, D.G., 1966 |
|||||||
|
Readme | About Us | Acknowledgement | How to Cite | Terms of Use | Ⓒ Rock Fracture Knowledgebase |
|||||||